

Furthermore, investigation of the strain rate sensitivity during the different steps of the failure indicates more sensitivity of the non-linear zone of the stress-strain curve with strain rate. The results show the important effect of strain rate on mechanical properties such that by increasing the strain rate, yield stress and ultimate stress were increased. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was applied to analyze the failure surface characteristics. The effect of high strain rate was analyzed through a servo-hydraulic machine, monotonic, and interrupted tensile tests ranging from 0.3 to 117.4 s-1. Regarding, samples based on urethane dimethacrylate resin material were printed in different directions (θ = ) and post-treatment was performed with respect to the UV and UV with temperature. In addition, the role of polymerization as a determining factor in the final mechanical properties of the SLA parts is indicated. This study investigates the effect of high strain rate on mechanical behavior, considering the fact that, materials can be shown different mechanical properties under rapid straining compared to quasi-static loading.
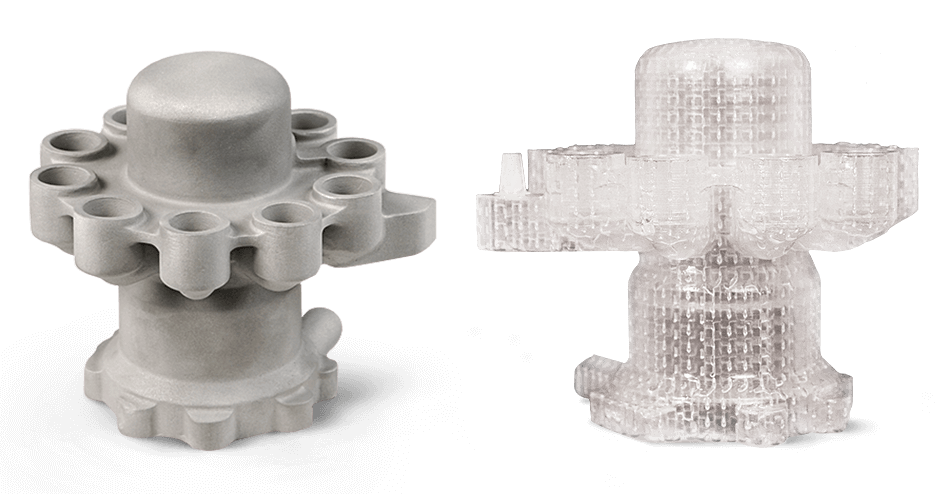
Stereolithography (SLA) is becoming an important fabrication method among the different additive manufacturing (AM) techniques. The dimensions in the Z direction were more accurate than in the X-Y directions, showing the smallest size deviations for height measurements and large deviations in the length, width, and diameter of the hole. The sphere roundness and angularity were found to be the most and least accurate geometric characteristics, respectively. Both printed and cast parts had twice as many deviations in geometry as in dimensions. Build angle and Layer thickness were identified to be the first and the second most impactful parameters, respectively, affecting both the dimensional and geometric accuracy of Castable Wax patterns and Al cast parts, with optimal values of 0 deg and 0.25 μm, respectively. Coordinate Measuring Machine measurements of deviations in the printed and cast parts were analyzed using the “Smaller-the-better” scheme in the two-step optimization method of Taguchi experiments. SolidCast simulation was used to design the orientation of casting feeder to achieve directional solidification.

Taguchi’s Design of Experiment was used to define the number of experimental runs. This study considers an experimental approach to study the effect of SLA printing parameters such as layer thickness, build angle, support structure density, and support touchpoint size on the dimensional accuracy and geometrical characteristics of the Castable Wax printed patterns and the Al cast parts. However, the effect of SLA printing parameters on the dimensional accuracy and geometric characteristics have not been studied thoroughly. Stereolithography is one of the important AM techniques mostly exploited in RIC due to its accuracy, smooth surface, and precision. In Rapid Investment Casting, these characteristics can be affected by the printing parameters of the Additive Manufacturing method used in the pattern production process. Dimensional accuracy and geometric characteristics of the manufactured parts bear significant importance in product assembly.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
